© Copyright 2026 ContentWrap. All Rights Reserved.
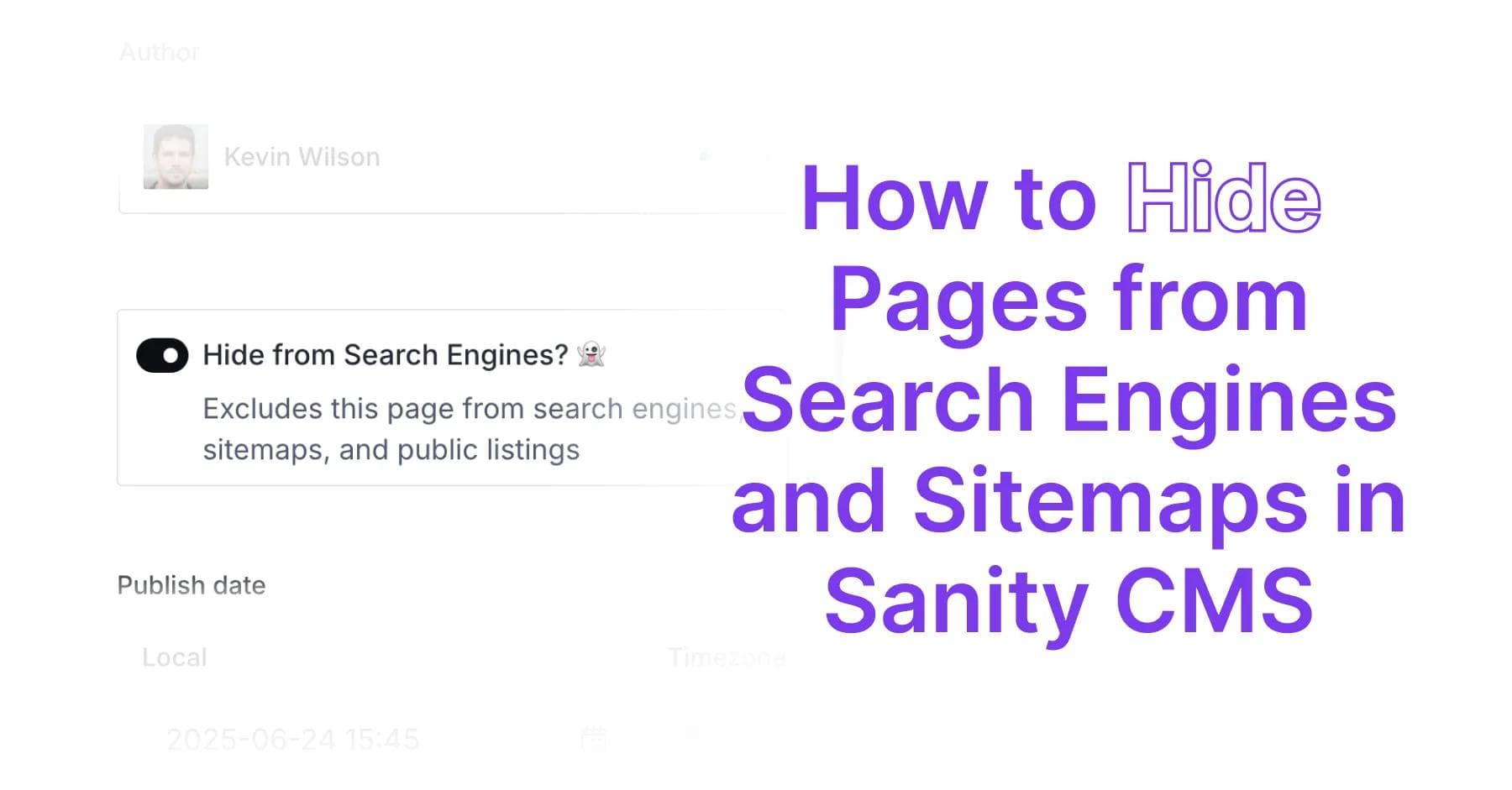
Have you ever needed to create content that shouldn't appear in search results? Whether you're testing new landing pages, creating client-specific content, or managing draft materials, there are countless scenarios where you need complete control over content visibility. While Sanity CMS provides powerful content management capabilities, it doesn't offer built-in functionality to hide pages from search engines and public discovery out of the box.
This comprehensive guide will show you how to implement a robust page visibility system that gives content creators full control over where their content appears. You'll learn to create a simple toggle that can hide pages from search engines, sitemaps, internal search results, and content listing pages with just one click.
By the end of this tutorial, you'll be able to:
Before starting this tutorial, you should have:
When we talk about "hiding" pages from search engines, we're actually implementing controls across four critical touchpoints:
Search engines like Google use robots meta tags to understand whether they should index a page. Setting robots: { index: false, follow: false } tells search engines not to include the page in their search results.
Sitemaps serve as a roadmap for search engines, listing all the pages on your website. Hidden pages should be completely excluded from your sitemap to prevent confusion for search engines.
Your website's internal search functionality should respect visibility settings. Users shouldn't find "hidden" content through your site's search feature.
Blog indexes, case study listings, and related content sections should automatically filter out hidden pages to maintain a clean user experience.
The key insight is that hiding content requires a coordinated approach across all these areas. A page isn't truly hidden if it appears in your sitemap but has no-index tags, or if it's excluded from search but still shows up in your blog listing.
The foundation of our visibility system is a simple boolean field that content creators can toggle. This field needs to be added to any document schema where you want visibility control.
Let's start by adding the hideFromSearch field to a blog schema:
import { DocumentIcon } from '@sanity/icons';import type { Rule } from 'sanity';export const blog = { name: 'blog', title: 'Blog Post', type: 'document', icon: DocumentIcon, fields: [ { name: 'title', title: 'Title', type: 'string', validation: (rule: Rule) => rule.required(), }, { name: 'slug', title: 'Slug', type: 'slug', options: { source: 'title', maxLength: 96, }, validation: (rule: Rule) => rule.required(), }, { name: 'hideFromSearch?', title: 'Hide from Search Engines', type: 'boolean', description: 'When enabled, this page will not appear in search engines, sitemaps, or public listings. Use for testing, private content, or draft materials.', initialValue: false, }, // ... other fields { name: 'content', title: 'Content', type: 'array', of: [{ type: 'block' }], }, ], preview: { select: { title: 'title', hideFromSearch: 'hideFromSearch', }, prepare(selection) { const { title, hideFromSearch } = selection; return { title: title, subtitle: hideFromSearch ? '🔒 Hidden from search' : '🌐 Public', }; }, },};For production use, you might want to add validation and conditional fields:
// Enhanced schema with additional controls{ name: 'seoSettings', title: 'SEO Settings', type: 'object', fields: [ { name: 'hideFromSearch', title: 'Hide from Search Engines?', type: 'boolean', description: 'Excludes this page from search engines, sitemaps, and public listings.', initialValue: false, }, { name: 'hideReason', title: 'Reason for Hiding', type: 'string', options: { list: [ { title: 'Testing/Draft Content', value: 'testing' }, { title: 'Client-Specific Content', value: 'client' }, { title: 'Seasonal/Temporary', value: 'seasonal' }, { title: 'Internal Use Only', value: 'internal' }, ], }, hidden: ({ parent }) => !parent?.hideFromSearch, validation: (rule: Rule) => rule.custom((value, context) => { const parent = context.parent as { hideFromSearch?: boolean }; if (parent?.hideFromSearch && !value) { return 'Please specify why this content is hidden'; } return true; }), }, ],}Create a reusable field definition that you can include across multiple document types:
export const visibilityField = { name: 'hideFromSearch', title: 'Hide from Search Engines', type: 'boolean', description: 'When enabled, this content will be excluded from search engines, sitemaps, and public listings', initialValue: false, group: 'seo', // If you're using field groups};// Usage in any schemaimport { visibilityField } from '../fields/visibility';export const caseStudy = { name: 'caseStudy', title: 'Case Study', type: 'document', fields: [ // ... other fields visibilityField, ],};Your XML sitemap serves as a roadmap for search engines. Hidden pages must be completely excluded to prevent search engines from discovering and potentially indexing them.
Here's how to modify your Next.js sitemap to respect the hideFromSearch field:
import type { MetadataRoute } from 'next';import { client } from '~/lib/sanity';type ContentItem = { slug: string; _updatedAt: string;};export default async function sitemap(): Promise<MetadataRoute.Sitemap> { const baseUrl = 'https://yourdomain.com'; // Static pages const staticPages = [ { url: baseUrl, lastModified: new Date(), changeFrequency: 'daily' as const, priority: 1, }, { url: `${baseUrl}/about`, lastModified: new Date(), changeFrequency: 'monthly' as const, priority: 0.8, }, { url: `${baseUrl}/blog`, lastModified: new Date(), changeFrequency: 'daily' as const, priority: 0.8, }, ]; // Dynamic content from Sanity const dynamicPages = await getDynamicPages(baseUrl); return [...staticPages, ...dynamicPages];}async function getDynamicPages(baseUrl: string): Promise<MetadataRoute.Sitemap> { try { const query = `{ "blogPosts": *[_type == "blog" && defined(slug.current) && hideFromSearch != true] { "slug": slug.current, _updatedAt }, "caseStudies": *[_type == "caseStudy" && defined(slug.current) && hideFromSearch != true] { "slug": slug.current, _updatedAt } }`; const { blogPosts, caseStudies } = await client.fetch<{ blogPosts: ContentItem[]; caseStudies: ContentItem[]; }>(query); const dynamicPages: MetadataRoute.Sitemap = []; // Add blog posts blogPosts.forEach((post) => { dynamicPages.push({ url: `${baseUrl}/blog/${post.slug}`, lastModified: new Date(post._updatedAt), changeFrequency: 'weekly', priority: 0.6, }); }); // Add case studies caseStudies.forEach((study) => { dynamicPages.push({ url: `${baseUrl}/case-studies/${study.slug}`, lastModified: new Date(study._updatedAt), changeFrequency: 'monthly', priority: 0.7, }); }); return dynamicPages; } catch (error) { console.error('Error generating dynamic sitemap:', error); return []; }}Meta tags tell search engines how to handle your pages. For hidden content, you need to set appropriate robots directives to prevent indexing.
Here's how to implement dynamic metadata that respects the hideFromSearch field:
import type { Metadata, ResolvingMetadata } from 'next';import { notFound } from 'next/navigation';import { client } from '~/lib/sanity';interface BlogPost { title: string; description: string; hideFromSearch: boolean; slug: string; author?: { name: string; }; image?: { url: string; alt: string; };}interface Props { params: { slug: string };}async function getBlogPost(slug: string): Promise<BlogPost | null> { const query = ` *[_type == "blog" && slug.current == $slug][0] { title, description, hideFromSearch, "slug": slug.current, "author": author->{name}, "image": { "url": image.asset->url, "alt": image.alt } } `; return client.fetch(query, { slug });}export async function generateMetadata( { params }: Props, parent: ResolvingMetadata): Promise<Metadata> { const post = await getBlogPost(params.slug); if (!post) { return { title: 'Post Not Found', robots: { index: false, follow: false, }, }; } const previousImages = (await parent).openGraph?.images || []; const baseMetadata: Metadata = { title: post.title, description: post.description, authors: post.author?.name ? [{ name: post.author.name }] : undefined, openGraph: { title: post.title, description: post.description, type: 'article', images: post.image?.url ? [post.image.url, ...previousImages] : previousImages, }, }; // Critical: Set robots meta tags for hidden content if (post.hideFromSearch) { baseMetadata.robots = { index: false, follow: false, }; } return baseMetadata;}export default async function BlogPostPage({ params }: Props) { const post = await getBlogPost(params.slug); if (!post?._id) { return notFound(); } return ( <article> <h1>{post.title}</h1> {/* Rest of your blog post content */} </article> );}Hidden pages must be excluded from all public-facing content lists, including blog indexes, related articles, search results, and navigation menus.
Here's how to modify your content fetching hooks to respect visibility settings:
import { cache } from 'react';import { client } from '~/lib/sanity';interface BlogPost { _id: string; title: string; slug: string; description: string; publishedAt: string; author: { name: string; slug: string; }; image?: { url: string; alt: string; };}interface UseBlogPostsOptions { limit?: number; offset?: number; authorId?: string; category?: string;}const getBlogPosts = cache(async (options: UseBlogPostsOptions = {}) => { const { limit = 10, offset = 0, authorId, category } = options; // Build dynamic filters let filters = ['_type == "blog"', 'hideFromSearch != true', 'defined(slug.current)']; if (authorId) { filters.push('references($authorId)'); } if (category) { filters.push('$category in categories[]->slug.current'); } const filterString = filters.join(' && '); const query = `{ "posts": *[${filterString}] | order(publishedAt desc) [${offset}...${offset + limit}] { _id, title, "slug": slug.current, description, publishedAt, "author": author->{ name, "slug": slug.current }, "image": { "url": image.asset->url, "alt": image.alt } }, "total": count(*[${filterString}]) }`; const params: Record<string, any> = {}; if (authorId) params.authorId = authorId; if (category) params.category = category; return client.fetch<{ posts: BlogPost[]; total: number; }>(query, params);});export async function useBlogPosts(options: UseBlogPostsOptions = {}) { return getBlogPosts(options);}You've successfully implemented a comprehensive page visibility system that gives content creators complete control over where their content appears. This system ensures that hidden pages are truly hidden across all touchpoints: search engines, sitemaps, internal search, and content listings.
The key benefits of this implementation include:
Consider extending this system with additional features:
By implementing this visibility system, you've created a powerful tool that enhances your content management workflow while maintaining complete control over what content appears in search engines and public listings. Your content creators now have the flexibility to test, iterate, and manage content visibility with confidence.
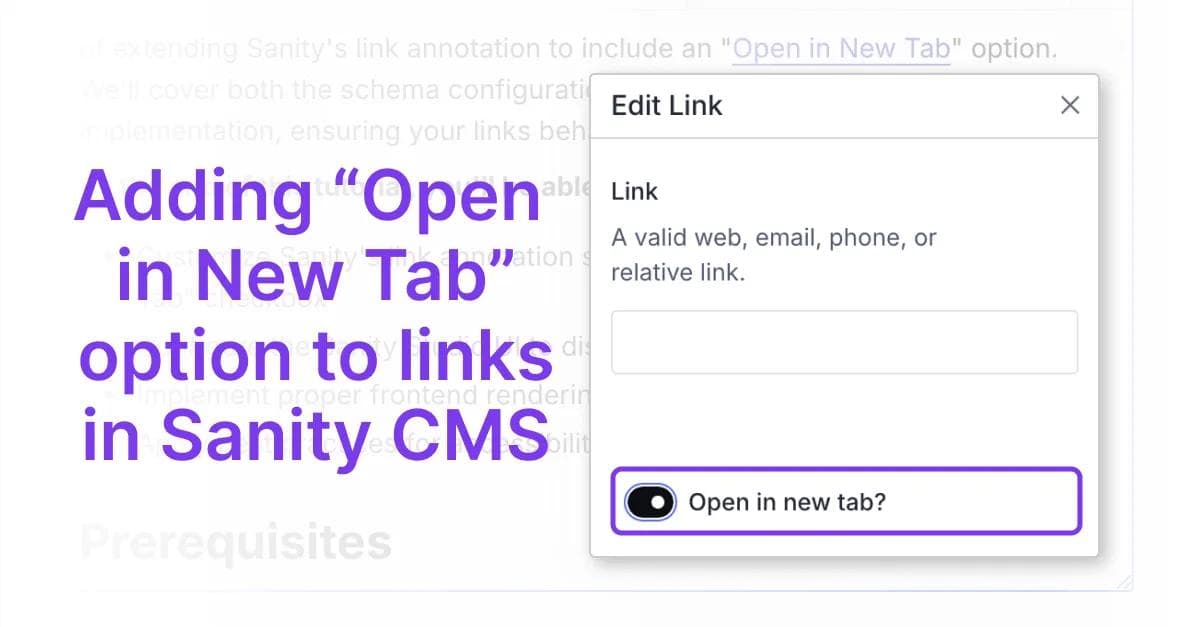
Learn how to add the missing "Open in New Tab" option to Sanity CMS links. This step-by-step guide shows you how to customize link annotations and properly implement frontend rendering for better content management.

Frustrated by Sanity's inability to wrap text around images? This tutorial shows you how to build a custom component that gives your content editors the power to float images left or right with adjustable width controls — just like Webflow.
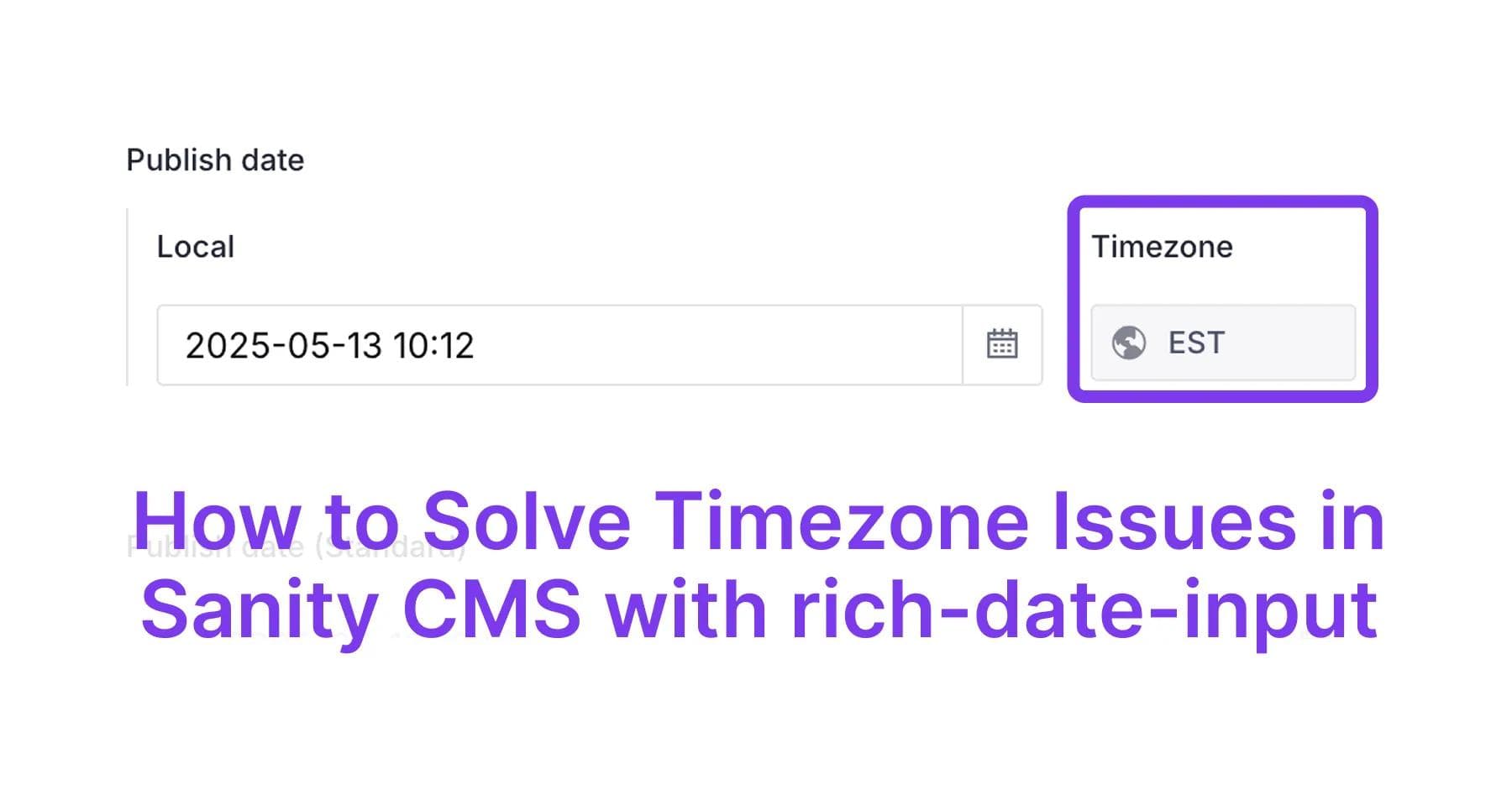
Eliminate timezone headaches in Sanity CMS with the rich-date-input plugin. Learn how to prevent publishing date confusion and ensure consistent datetime display for global teams with this simple yet powerful solution.